
Policy Update
How States Are Improving Endangered Species Protections in 2024
May 16, 2024
Overview
As one-third of American wildlife species face extinction, more states are ramping up legislative efforts to increase protections for threatened and endangered species within their borders. In 2024, at least 14 states introduced 24 bills to improve endangered species protections.
Why Endangered Species Matter
Approximately 1,000,000 wildlife species – and a third of the species in the U.S. – currently face extinction, primarily due to human-caused forces such as habitat degradation, invasive species, and climate change. A mass wildlife extinction event will have far-reaching negative impacts; many endangered species provide crucial ecosystem services that keep natural environments healthy, support the well-being of human communities, and provide a range of economic value.
- How SESAs Can Help: While many endangered species receive federal protection, state endangered species acts (or SESAs) allow states to provide protection to species unique to that state and to act more swiftly in strengthening protection for at-risk species within their borders. A strong SESA can also serve as a complement to the federal ESA, which has been susceptible to rollbacks in previous years.
- Digging Deeper: Last year, NCEL released a report outlining the efficacy of SESAs in mitigating the biodiversity crisis as well as the barriers to passing SESAs. State SESAs are an important tool to both protect at-risk species by preventing federal listings and filling gaps from the federal Endangered Species Act.
State of Play – Which States Are Strengthening Endangered Species Protections?
Of the 14 states that considered endangered species legislation in 2024, many focus specifically on expanding or strengthening their state endangered species acts (SESAs). As of May, at least three states have enacted laws: Maryland, Pennsylvania, and Washington.
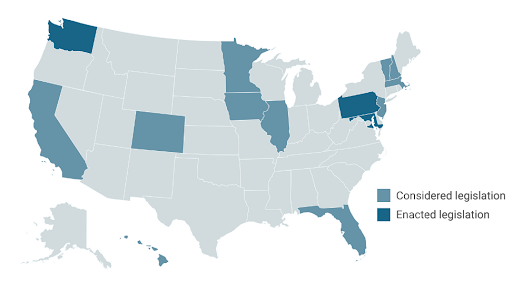
- Maryland enacted H.B.0345/S.B.0916 in May which will 1) expand the definition of “fish” and “wildlife” to allow for a wider range of species to receive protection, 2) require the Maryland Department of Natural Resources to review its endangered species list and consider new species for listing at least once every five years, and 3) authorize citizens to file petitions requesting the listing of a species as threatened or endangered.
- Pennsylvania S.B.709 recently became public law and will increase penalties for actions that result in the death of bald or golden eagles (both of which are federally protected).
- Washington enacted S.B.5950, an appropriation bill that allocates $22 million for the protection, recovery, and restoration of biodiversity with a focus on threatened and endangered species
Other Noteworthy Legislation
- Colorado H.B.24-1117 has been sent to the governor and would include invertebrates and plants in the state endangered species list if enacted.
- New Hampshire S.B.390 would update the state definition of “critical habitat” to be consistent with federal standards.
- Minnesota S.B.3631 has passed the first chamber and would create a “threatened” category for species protection.
- Vermont H.812 would mandate the declaration of critical habitat for endangered species and revise the endangered species list every three years.
- New Jersey A.1817 would add protections for threatened plant species and require developing a list of threatened plant species within one year of the bill’s passage.
Stay Informed on State Policy With NCEL
Stay up to date on trends in endangered species policy across the country this year with NCEL’s Bill Tracking Map.